Google Shopping: what is it and why your eCommerce business needs it
As a platform, Google has so much to offer. From their search engine to the Google Ads platform and hundreds of services in between, it is no surprise that they are considered the third biggest tech giant in the world, just after Apple and Microsoft.
Google Shopping is just another string in their bow – and another tool that can support your eCommerce business. But what is Google Shopping, and how can it help you?
Whether you’re just getting started with Google Shopping or you’re a well-seasoned marketing specialist, this article will explore strategies you can implement today to boost your eCommerce business.
What is Google Shopping?
Invented in 2002 and previously known as Google Product Search as well as Google Products and Froogle (anyone been in the Marketing game long enough to remember Froogle?), Google Shopping allows people to easily see product listings across various vendors’ sites at once, comparing prices as they go.
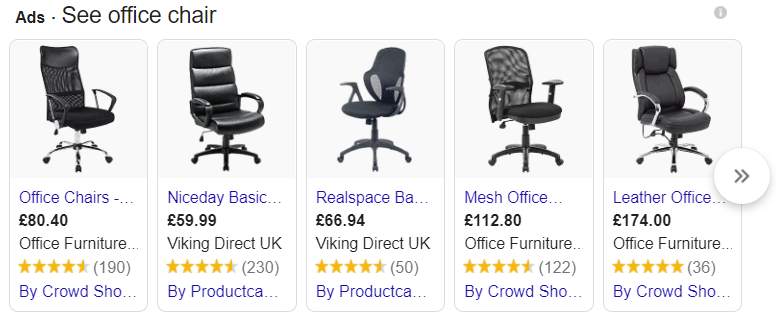
36% of all product searches originate on Google – this means that 36% of potential customers start their purchasing journey on that very platform. This is why it is essential to get on board with services like Google Shopping.
Since 2012, digital marketers have been able to use Google Shopping as a paid advertising model for their business.
So, what is Google Shopping?
Google Shopping ads can appear in Google search results, on the Shopping tab, on search partner websites, in the price comparison Shopping service and apps, on the Google Display Network, and even on YouTube. By using Google Shopping ads as part of your wider marketing strategy, you can leverage the benefits of having a wider reach and greater brand exposure.
In October 2020, Google also announced the launch of their free Google Shopping Ad listings. Although these free Shopping listings may be a great way to drive additional traffic to your eCommerce website, there is much less control compared to paid Shopping ads. To get the most out of your Google Shopping campaigns, you will want to establish a thorough PPC campaign that incorporates Shopping ads.
By using Google Shopping, your product listings are visible before someone even lands on your site. Google Shopping listings can also provide users with more information than text-based search ads such as a product image and brand, pricing, and shipping information.Other enhancements include merchant promotions, product ratings, Google review information or grouping products together as Showcase Shopping ad groups. As a result, Shopping ads are great for engaging with potential customers that have a strong purchase intention.
Why you should use Google Shopping
If you don’t already use Google Shopping for your eCommerce business, it is well worth getting in on the action. As a form of pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, Google Shopping can be a cost-effective and important way to advertise your business online.
This type of advertising operates on a “pay-to-play” model where merchants pay Google to list their products. Whether your product listing appears in the search results is then influenced by both relevance and the bid amounts paid. Google says that this allows them to “deliver the best answers for people searching for products and help connect merchants with the right customers”.
In short, Google Shopping is another way of helping your business show up online. By using Google Shopping as part of your PPC strategy, your business has the potential to be visible in search results as an organic search result, as a text-based paid search ad, and as a Google Shopping result.
On top of this, Product Listing Ads (PLAs) run through Google Shopping account for 60% of all Google Ads clicks – according to the Q4 2019 Digital Marketing Report by Merkle.
Google Shopping allows you to target customers who already know what they want – meaning you are reaching people with a higher purchase intent. Shopping ads appear at the top of the screen, above the general text-only search results, and are eye-catching in their image-based nature. They grab the user’s attention, and, in turn, these users tend to convert into customers.
Getting started with Google Shopping ads
If you are still new to this type of advertising, you might be wondering what is a Google Shopping campaign?
In a nutshell, this is the entire process for getting started with Google Shopping ads:
- Set up a Google Merchant Center account
- Verify website
- Link to your Google Ads account
- Create your shopping feed
- Optimise your shopping feed
- Build product groups
- Set up the delivery template
- Create Google Shopping campaign in Google Ads
- Build ad groups
- Optimise Shopping campaign with bid adjustments
Setting up Google Shopping campaigns can be a seemingly straightforward task. The most basic approach to setting up a Shopping account is to create one campaign, add one Ad Group, then divide your product groups out. While this is easy to manage, if you are still using this approach you’re missing out on some incredible opportunities for optimisation.
If you really want to get the most out of your Shopping campaigns, you’ll want to look at formulating a strategic approach that ensures you get the best possible return on your ad spend.
Advanced strategies for Google Shopping
There are certain strategies you can employ to make sure you are getting the most out of your Google Shopping campaigns. As a starting point, you should always consider search intent – also known as user intent – as one of your main priorities when developing Shopping campaigns.
User intent
All customers follow a specific journey when shopping. This journey comprises 5 stages:
- Awareness
- Interest
- Intent
- Consideration
- Purchase
At various points throughout the customer journey (or marketing funnel), people may drop off the path either because they no longer decide to purchase the product or because they decide to shop with a competitor brand. User intent refers to how likely an individual is to purchase a product and can be determined in relation to the customer journey – the further along the customer journey someone is, the more likely they are to make a purchase.

Therefore, the more your page (or in this case your product) satisfies search intent, the higher it will rank within Google Shopping listings.
You can optimise your Google Shopping PLAs for user intent by undertaking keyword research to create product feed titles and descriptions tailored to people with a high purchase intent. This, in turn, can help increase conversions for your PLAs.
For example, creating a Shopping campaign based on specific product names or SKUs will align with higher search intention than creating a Shopping campaign based on generic product categories.
Once you’ve set up your Google Shopping ads based on intent, you will then want to further control intent through Negative Keyword Lists. This will prevent your Shopping campaigns from competing with each other by stopping your PLAs from showing up when certain search terms are used.
You can then use campaign priority settings to indicate which campaigns Google should prioritise when delivering your PLAs. On both Google Ads and Bing Ads, each shopping campaign has a priority setting of low, medium, or high. This priority setting only works if there are two or more shopping campaigns containing the same products. So, if you have multiple campaigns based on search intent level, you should adjust the campaign priority to prioritise product lists with a higher intent.
Query-level bidding
Similar to bidding based on user intent, another advanced strategy worth executing is query-level bidding.
Query-level bidding allows you to bid both quickly and easily depending on the search queries you are targeting. Briefly, it involves bidding low for general search queries, and placing higher bids for specific or branded search queries.
The core components involved in engaging query-level bidding for shopping campaigns are:
- Priority settings
- Negative keywords
- Product bids
- Shared budgets
When using query-level bidding, the Priority Setting will inform Google Shopping which campaign should be used prioritised for a particular query. Next, the Negative Keywords will filter the queries into the correct campaign and prevent them from showing in the other campaigns. The product bids will inform Google how much you are willing to spend on that query. Finally, the Shared Budget ensures all your campaigns work together in harmony to achieve the best return on investment.
Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA)
RLSA, or Remarketing Lists for Search Ads, allows advertisers to tailor their search campaigns based on whether a user has previously interacted with their website, or specific pages on their site.
Remarketing adverts are a key component in re-engaging previous website visitors who may have visited your online store but didn’t complete a purchase. As a result, incorporating remarketing lists into your PPC strategy is vital for ensuring your PPC and Google Shopping campaigns are successful.

With RLSAs, you can create Shopping campaigns that are highly targeted towards people who are most likely to make a purchase. Shopping remarketing lists offer the ability to segment your site visitors by previous site engagement. You can then use RSLAs to create Shopping campaigns for various user groups based on their previous site engagement, such as ‘abandoned shopping carts’, ‘loyal customers’ or ‘repeat visitors’.
If you’re using Smart Bidding like Target ROAS, segmenting your ad audience with remarketing lists can also help you to achieve a higher return on investment.
Customer match data
Customer Match Data bidding works in a similar manner to RLSAs. While RLSAs use tracking code to create remarketing audiences based on website activity, customer match data allows you to target customers by uploading customer information into Google Ads.
Customer match data is a useful tool for increasing brand awareness, re-engaging previous customers, or turning offline visitors into online customers. Within the Google Shopping network, you can use customer match data to optimise your campaigns by adjusting your bid for different customer list uploads.
Google Customer Match Data is designed to help retailers reach their “highest-value customers” by strengthening your connections with your previous visitors on the Google Search platform. However, it can also be a powerful strategy for nurturing leads by ensuring your Shopping ads are visible whilst they are browsing YouTube or visiting websites that are part of Google’s Display Network.
Geo-targeting
If your eCommerce business has various store locations, or only ships to certain locations, geo-targeting can be an ideal way to optimise your Google Shopping campaigns and minimise the risk of wasted ad spend.
Geography-based bid adjustments or modifiers allow advertisers to change bid percentages based on locations. You can then use these geo-targeting settings to refine the geographic locations where your Shopping ads are displayed.
As mentioned, this is a great opportunity to target people based on your physical store location. You can also use geography based bid adjustments to exclude unwanted regions such as regions you don’t ship to or to target individuals in locations that have been identified as having a higher user intent or higher conversion value.
Smart Shopping campaigns
In a world where AI is taking the lead, Smart Shopping is one of Google’s newest campaign types. Smart Shopping campaigns used machine-learning to optimise your Shopping ads whilst also reducing the manpower needed to manage those ads.

If you choose to run Smart Shopping campaigns, all you need to do when setting up your Shopping PLAs is to enter your campaign objective and budget – Smart Shopping will then take care of the rest with automated bidding and ad placements.
Smart Shopping ads are often a preferred choice for eCommerce advertisers who have smaller budgets or less time to strategically manage their PPC advertising campaigns.
However, Smart Shopping campaigns aren’t without their faults. Due to their machine-led nature, there are a number of restrictions with Smart Shopping campaigns. When you run Smart Shopping campaigns, you lose the ability to control Shopping ads with Negative Keyword management. You will also be unable to determine attribution or make product adjustments within your campaigns.
Smart Shopping campaigns do have their place within pay per click advertising, and under certain circumstances can work well. However, in most circumstances you will achieve far greater results by implementing granular changes and advanced strategies to your Google Shopping campaigns.
If you’re still wondering “What is Google Shopping and How can I get the best results from my Google Shopping campaigns?”, hiring an experienced PPC management company means you can leverage their expertise to boost your PPC performance.
Performance metrics to measure for Google Shopping
The best thing about Google Shopping campaigns — and any PPC campaign for that matter — is that they can be measured, tested, and optimised.
As with any paid advertising campaign, it is important to analyse your results. This way you know where to spend your money in terms of future campaigns, what improvement can be made to your current campaigns, and what to avoid next time.
Within the Google Ads platform itself, there is a plethora of data you can use to determine the success of your Shopping campaigns. From cost-per-click to search impression share and conversion rate, there are several key PPC performance metrics you will want to keep an eye on.
Cost-per-click (CPC) shows how much money each individual click on your Shopping ad is costing your business. By analysing your CPC and refining your campaigns, you will be able to reduce your average CPC.
Metrics relating to your conversions — such as conversion rate and total conversions — allow you to see which particular Google Shopping campaigns or product groups result in sales. You can use this data to determine which campaigns are underperforming and make informed adjustments to improve the performance of those campaigns.
By using Google Merchant Center, as well as Google Analytics, you can access further performance metrics such as click data, sessions, transactions and more. By analysing these, you can gain a deeper understanding of the success of your Google Shopping campaigns. This ensures you are getting your money’s worth from each campaign.
Boost your eCommerce business with Google Shopping
Google Shopping really is an incredible way to utilise PPC advertising for eCommerce businesses. By promoting your products in this way, you are simply putting your business at the forefront of search results across the globe.
Here at Common Ground, we are passionate about developing sophisticated Shopping campaigns that boost your eCommerce business. Interested in learning more? Contact us today!


